-
SUMMARY
-
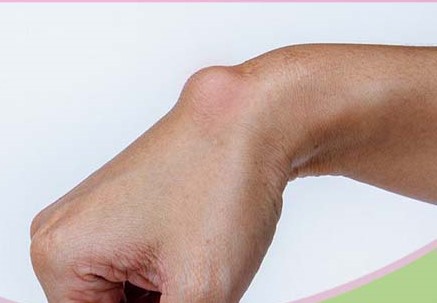
Ganglion Cysts are mucin-filled synovial cysts and are the most common masses found in the wrist and hand.
-
Diagnosis can be made clinically with a firm and well circumscribed mass that transilluminates.
-
Treatment can be observation for majority of ganglions. Surgical excision is indicated for ganglion cysts associated with severe symptoms or neurovascular manifestations.
-
-
EPIDEMIOLOGY
-
Incidence
-
common
-
most common hand mass (60-70%)
-
-
-
Anatomic location
-
dorsal carpal (70%)
-
originate from SL articulation
-
-
volar carpal (20%)
-
originate from radiocarpal or STT joint
-
- volar retinacular (10%)
-
originate from herniated tendon sheath fluid
-
-
dorsal DIP joint (mucous cyst, associated with Heberden's nodes)
-
may also occur in the lower extremity
-
most commonly about the knee
-
-
-
-
ETIOLOGY
-
Mechanism
-
trauma
-
mucoid degeneration
-
synovial herniation
-
-
Pathophysiology
-
filled with fluid from tendon sheath or joint
-
no true epithelial lining
-
-
Associated conditions
- median or ulnar nerve compression
-
may be caused by volar ganglion
-
-
hand ischemia due to vascular occlusion
-
may be caused by volar ganglion
-
- median or ulnar nerve compression
-
-
PRESENTATION
-
Symptoms
-
usually asymptomatic
-
may cause issues with cosmesis
-
-
Physical exam
-
inspection
-
transilluminates (transmits light through tissue)
-
-
palpation
-
firm and well circumscribed
-
often fixed to deep tissue but not to overlying skin
-
-
vascular exam
-
Allen's test to ensure radial and ulnar artery flow for volar wrist ganglions
-
-
-
-
IMAGING
-
Radiographs
-
normal
-
-
MRI
-
indications
-
not routinely indicated
-
-
findings
-
shows well marginated mass with homogenous fluid signal intensity
-
-
-
Ultrasound
-
useful for differentiating cyst from vascular aneurysm
-
may provide image localization for aspiration while avoiding artery
-
-
-
HISTOLOGY
-
Biopsy
-
indications
-
not routinely indicated
-
-
findings
- will show mucin-filled sac with no true epithelial/synovial lining
- will show mucin-filled sac with no true epithelial/synovial lining
-
-
-
TREATMENT
-
Nonoperative
-
observation
-
indications
-
first line of treatment in adults
- children
-
76% resolve within 1 year in pediatric patients
-
-
-
-
closed rupture
-
home remedy
-
high recurrence
-
-
aspiration
-
indications
-
second line of treatment in adults with dorsal ganglions
-
aspiration typically avoided on volar aspect of wrist due to radial artery
-
-
outcomes
- higher recurrence rate (50%) than surgical resection but minimal risk so reasonable to attempt
- higher recurrence rate (50%) than surgical resection but minimal risk so reasonable to attempt
-
-
-
Operative
-
surgical resection
-
indications
-
technique
-
requires adequate exposure to identify origin and allow resection of stalk and a portion of adjacent capsule
-
at dorsal DIP joint: must resect underlying osteophyte
-
-
results
-
volar ganglions have higher recurrence after resection than dorsal ganglions (15-20% recurrence)
-
-
-
-
-
COMPLICATIONS
-
With aspiration
-
infection (rare)
-
neurovascular injury
-
-
With excision
-
infection
-
neurovascular injury (radial artery most common)
-
injury to scapholunate interosseous ligament
-
stiffness
-
-