SUMMARY
-
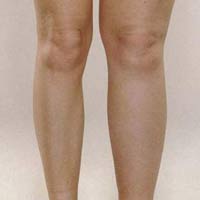
emihypertrophy is an idiopathic condition that can also be caused by a variety of syndromes, and presents with asymmetry between the right and left sides of the body to a greater degree than can be attributed to normal variation.
-
Diagnosis is made clinically with abnormal asymmetry defined as a 5% or greater difference in length and/or circumference.
-
Treatment is observation with or without shoe lifts for leg length differences < 2 cm at skeletal maturity. Surgical intervention is indicated for leg length differences > 2 cm, with different techniques depending on the discrepancy magnitude and remaining skeletal growth.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
-
Pathophysiology
-
most common causes are
-
idiopathic (non-syndromic)
-
syndromic
-
neurofibromatosis
-
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
-
Klippel-Trenauney syndrome
-
Proteus syndrome
-
-
-
-
Associated conditions
-
orthopaedic manifestations
-
scoliosis (compensatory)
-
peripheral nerve entrapment (rare)
-
-
medical conditions & comorbidities
-
malignant intra-abdominal tumors
-
Wilm's tumor (most common)
-
perform serial abdominal ultrasounds (every 3 months) until age 7 to rule out Wilm's tumor
-
then physical exam every 6 months until skeletal maturity
-
-
adrenal carcinoma
-
hepatoblastoma
-
-
genitourinary abnormalities
-
medullary sponge kidneys
-
polycystic kidney
-
inguinal hernias
-
-
-
CLASSIFICATION
-
-
Congenital classification
-
congenital
-
total
-
involvement of all organ systems
-
-
limited
-
only muscular, vascular, skeletal, or neurologic involvement
-
classic (ipsilateral upper and lower limbs)
-
segmental (a single limb)
-
facial
-
crossed
-
-
-
-
acquired
-
very rare
-
can result from injury, infection, radiation or inflammation
-
-
-
Syndromic classification
-
non-syndromic (isolated)
-
syndromic (part of a clinical syndrome)
-
-
-
PRESENTATION
-
Physical exam
-
findings rarely apparent at birth, manifest during growth
-
skin often thicker on involved side
-
more hair on corresponding side of the head
-
limb circumference asymmetric
-
leg-length discrepancy (LLD)
-
-
-
IMAGING
-
Radiographs
-
AP + lateral of affected limb may demonstrate enlargement of bone and soft tissue
-
osseous maturation may be seen
-
-
-
Abdominal ultrasound
-
indications
-
perform serial abdominal ultrasounds (every 3 months) until age 7 to rule out Wilm's tumor
-
-
-
STUDIES
-
Renal function tests
-
Serum alpha-fetoprotein
-
screen for embryonal tumors
-
TREATMENT
-
Nonoperative
-
observation, shoelift, corrective shoes
-
indications
-
< 2 cm projected LLD at maturity
-
-
-
-
Operative
-
surgical correction
-
indications
-
based on principles of leg length discrepancies
-
-
-