_moved.jpg)
SUMMARY
-
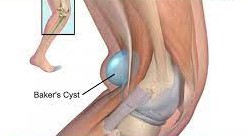
Popliteal Cysts are common soft tissue masses in children that unlike the adult population, are most often not associated with meniscal tears.
-
Diagnosis is suspected clinically with a palpable mass in the popliteal fossa that transilluminates. MRI can confirm the diagnosis of a cystic lesion.
-
Treatment is observation as the majority of lesions spontaneously resolve.
ETIOLOGY
-
Pathoanatomy
-
popliteal cysts usually are located
-
between muscles of
-
semimembranosus
-
medial head of gastrocnemius
-
-
from herniated posterior knee joint capsule synovium
-
-
ANATOMY
-
-
Muscles posterior to medial knee capsule
-
semimembranosus
-
medial head of gastrocnemius
-
-
PRESENTATION
-
Symptoms
-
usually asymptomatic
-
-
Physical exam
-
located in popliteal fossa
-
usually located medially and distal to knee crease
-
most pronounced with knee extended
-
-
-
mass will transilluminate
-
IMAGING
-
Radiographs
-
are normal
-
-
Ultrasound
-
consistent with cystic lesion
-
-
MRI
-
show fluid filled cyst
-
TREATMENT
-
Nonoperative
-
observation
-
indications
-
mainstay of treatment
- with majority of cases resolving spontaneously
- with majority of cases resolving spontaneously
-
-
-
-
Operative
-
excision
-
indications
-
only if cyst causes significant discomfort
-
failure of spontaneous resolution
-
-
-